Introduction
Materials and Methods
1. Changes in light transmittance of covering materials by PM exposure
2. Cucumber cultivation under light transmittance reduction treatment in a greenhouse
3. Statistical analysis
Results and Discussion
Conclusion
Introduction
In recent years, air pollution including small particles and gaseous pollutants has become a growing concern for both human beings and the environment. Among the small particles floating in the air, the particles with size in the range of 0.001-100 µm are called particulate matter (PM) (Popek et al., 2018). PM is composed of various organic and inorganic compounds and it varies depending on the source. PM can occur naturally, but a significant amount of PM is produced by human activity. PM is generated anthropogenically through automobile exhaust and fossil fuel combustion (Oh, 2016).
Airborne PM can cause respiratory illness and cancer when absorbed by the human body, adhere to plant leaves and reduce stomatal activity, or be absorbed into the soil and stressed the crops (Daresta et al., 2015). Crops in facilities are not directly affected by PM, but they are adversely affected by it. When the ionic components of PM are wetly attached to the covering material, they leave a white coating on the covering material when it dries, reducing light transmittance and internal temperature (El-Shobokshy and Hussein, 1993; Sim and Song, 2019; Lee et al., 2022). PM attached to the covering material is mainly removed by rainfall. In Korea, the contamination of covering materials by PM can be a problem due to frequent yellow dust and fewer rainfall days during the spring season (Chun et al., 2002a; Aristizábal et al., 2012; KMA, 2023). Sunlight and temperature are critical to plant growth and development, therefore, a change in light and temperature in a greenhouse due to the contamination of covering material can have a negative effect on crop yields (Chun et al., 2002b; Kitta et al., 2012).
Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) is one of the important fruit vegetables cultivated in greenhouses and a highly profitable crop in Korea. Optimum growing temperatures are 22-28°C during the day and 15-18°C during the night, with heat stress occurring at temperatures above 35°C (RDA, 2018b). Although cucumber has a low light compensation point, prolonged lack of sunlight has a negative effect on yield and fruit quality as it harvests fruits continuously throughout the growing season (Kitta et al., 2012; RDA, 2018a). Chun et al. (2002b, 2002c) investigated the growth and yield of pumpkin and cucumber grown in greenhouse farms and confirmed that the reduced light transmittance condition caused elongated nodes and decreased yields. Several studies have been conducted to enhance the growth of cucumber through supplemental lighting in a greenhouse (Hao and Papadopoulos, 1999; Hao et al., 2018).
During the spring season in Korea, the number of days with PM increases due to the occurrence of yellow dust. High levels of PM reduce the transmittance of covering materials in greenhouses, however, there is a few researches on the changes in the light transmittance of covering materials and the crop yield in a greenhouse as affected by PM occurrence. In this study, we confirmed the changes in the light transmittances of the greenhouse covering materials, PE and PO, in accordance with the occurrence of PM. Also, we investigate the growth and yield of cucumber grown in a greenhouse with the reduced light transmittance during the spring season.
Materials and Methods
1. Changes in light transmittance of covering materials by PM exposure
Commercially available polyethylene (PE) film and polyolefin (PO) film were used as the covering materials. PE and PO films were exposed to test PM (Arizona Test Dust 0-5 μm, PTI, USA) in the transparent acrylic chamber (36×36× 57 cm). When the chamber is running, the three fans on the ceiling of the chamber rotate, blowing PM in the cups below the fans into the chamber. The films were exposed to PM 0.79±0.053 g·m-2 per hour in the chamber. The light transmittance was calculated by measuring the light intensity under the PE and PO films before and after the PM exposure using a light meter (LI-250A Light Meter, LI-COR Inc., Nebraska, USA).
2. Cucumber cultivation under light transmittance reduction treatment in a greenhouse
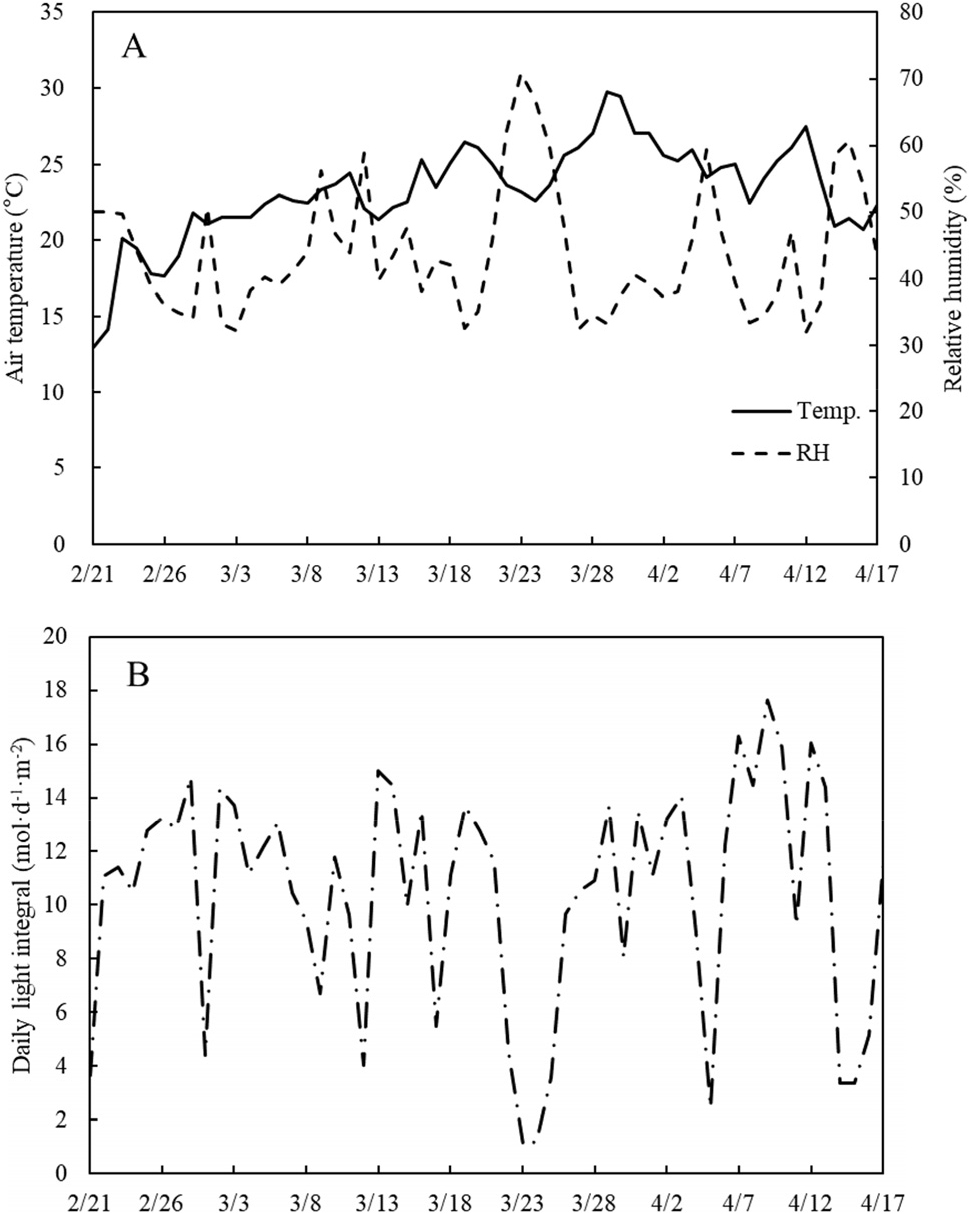
The seedlings of ‘Sindong’ cucumber (Haeoreumjongmyo, Asan, Korea) were transplanted in the greenhouse located at Protected Horticulture Research Institute, National Institute of Horticultural and Herbal Science. The cultivation of cucumber was conducted from February 20 to April 17, 2023, and the mean daily air temperature and relative humidity during the cultivation period were 23±3.18℃ and 44±9.60%, respectively (Fig. 1). In order to investigate the cucumber growth under the reduced light transmittance conditions, we installed the PE tunnels with different light transmittance in the greenhouse. The light transmittances of PE tunnels were controlled artificially by applying dust and adhesive material, and those were reduced by 10, 20, and 30%, respectively. During the cultivation period, we removed periodically tendrils and lateral branches, and maintained one fruit per each node and the plants were drip-irrigated with the nutrient solution (Daeyu Mulpure No. 2, Daeyu Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea) of EC 1.5 dS·m-1 and pH 6.5. The plant height, stem diameter, number of leaves, leaf area, SPAD value, fresh and dry weight of shoot, and fruit yield of cucumber plants cultivated in the 0 (control), 10, 20, and 30% light transmittance reduction treatments were investigated.
3. Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using the SAS program (Enterprise Guide 8.3, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Duncan's multiple comparison test was used to determine significant differences (p < 0.05) between treatments, and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to assess the results.
Results and Discussion
The light transmittance of PE and PO films decreased with increasing the time of PM exposure in the chamber (Fig. 2). Before the exposure of PM, the light transmittances of PE and PO films were 82.8 and 85.0%, respectively. After 84 hours of continuous exposure to PM, the light transmittances of PE and PO films decreased by 16.7 and 12.8%, respectively, compared to before the exposure. At the same exposure time, PE film showed a higher reduction in light transmittance than PO film. PO films have the higher light transmittance than PE films (Kwon et al., 2014; Moon et al., 2020) and is advantageous in terms of light transmittance due to its lower level of fine dust adhesion.
The plant height and leaf area of cucumber plants tended to increase as the reduction in light transmission increased (Fig. 3). At 56 days after transplanting, the plant height, leaf length and width, leaf area, and shoot fresh weight were highest in the 30% reduced light transmittance treatment, however, the stem diameter, number of leaves, and root fresh weight were not significantly different among the treatments (Table 1, Fig. 4). Smith et al. (1984) and Abu-Zahra et al. (2016) reported that shading resulted in longer plant height and larger foliar area of cucumber, indicating that shading affected cucumber growth. The previous study (Smith et al., 1984) reported that shading conditions increase shoot fresh weight in cucumber, which is consistent with our results, but Nikolaou et al. (2018) reported a delay in cucumber growth.
Table 1.
Stem diameter, number of leaves, leaf length and width, and SPAD value of cucumber plants grown in the control, 10, 20, and 30% reduced light transmittance treatments for 56 days after transplanting.
| DAT | Treatment |
Stem diameter (mm) |
No. of leaves (/plant) |
Leaf length (cm) |
Leaf width (cm) | SPAD value |
| 7 | Control | 3.40 bz | 2.33 a | 4.53 a | 5.55 b | 44.67 ab |
| –10% | 3.35 b | 2.00 a | 4.25 a | 5.20 b | 49.10 a | |
| –20% | 4.02 a | 2.00 a | 4.33 a | 5.85 ab | 41.93 b | |
| –30% | 3.78 ab | 2.00 a | 4.27 a | 6.43 a | 41.85 b | |
| 14 | Control | 4.57 a | 3.33 a | 6.75 a | 7.32 a | 32.45 a |
| –10% | 4.04 a | 3.00 a | 6.57 a | 7.53 a | 30.40 a | |
| –20% | 3.94 a | 3.00 a | 5.95 a | 6.87 a | 31.33 a | |
| –30% | 4.12 a | 3.00 a | 6.15 a | 7.62 a | 33.70 a | |
| 21 | Control | 7.92 a | 6.17 b | 14.27 b | 17.58 b | 31.68 a |
| –10% | 7.84 a | 6.00 b | 14.85 ab | 18.12 b | 32.25 a | |
| –20% | 8.78 a | 7.00 a | 16.85 a | 21.35 a | 33.07 a | |
| –30% | 8.17 a | 6.67 ab | 16.43 ab | 20.90 a | 30.58 a | |
| 28 | Control | 7.64 a | 9.67 a | 18.58 a | 22.53 a | 30.18 a |
| –10% | 8.01 a | 8.17 b | 19.18 a | 22.83 a | 31.38 a | |
| –20% | 7.96 a | 7.67 b | 19.65 a | 22.90 a | 31.00 a | |
| –30% | 8.69 a | 8.50 ab | 19.63 a | 24.30 a | 31.23 a | |
| 34 | Control | 9.63 b | 15.50 a | 29.08 a | 21.77 a | 30.80 b |
| –10% | 11.11 a | 15.67 a | 31.07 a | 23.38 a | 32.10 ab | |
| –20% | 9.65 b | 15.33 a | 29.60 a | 22.67 a | 33.80 a | |
| –30% | 9.10 b | 14.50 a | 31.00 a | 22.77 a | 34.18 a | |
| 42 | Control | 11.63 a | 21.33 a | 26.70 a | 33.77 b | 40.32 a |
| –10% | 11.95 a | 20.67 a | 27.27 a | 37.63 a | 37.05 a | |
| –20% | 10.73 a | 20.50 a | 26.25 a | 37.90 a | 35.45 a | |
| –30% | 10.88 a | 21.33 a | 27.93 a | 37.32 a | 36.38 a | |
| 48 | Control | 12.50 a | 27.00 a | 26.97 b | 35.73 c | 54.23 ab |
| –10% | 12.65 a | 28.17 a | 28.48 ab | 36.97 bc | 55.02 a | |
| –20% | 12.48 a | 25.16 a | 29.33 a | 28.77 ab | 50.93 bc | |
| –30% | 13.77 a | 25.83 a | 30.25 a | 39.90 a | 49.03 c | |
| 56 | Control | 13.76 a | 26.67 a | 27.67 b | 33.58 c | 45.92 a |
| –10% | 12.97 a | 27.67 a | 29.77 ab | 35.80 b | 46.35 a | |
| –20% | 12.87 a | 26.50 a | 29.58 ab | 37.70 ab | 47.88 a | |
| –30% | 12.82 a | 26.50 a | 31.12 a | 39.4 3a | 46.37 a |
The numbers of cucumber fruits were 24.7, 23.3, 26.5, and 22.4 fruits/m2 for the control, 10, 20, and 30% reduced light transmittance treatments, respectively. The cumulative yield of cucumber during the cultivation period was highest in the control and the reduction of light transmittance decreased the cucumber yield (Fig. 5). At 56 DAT, the cumulative yield of cucumbers in the control was 7.3 kg·m-2, and that in the 30% reduced light transmittance treatment was 5.6 kg·m-2, which was reduced by 24% compared to the control. In the previous study, it was reported that 30% shading reduced the individual fruit weight of cucumber which resulted in the total yield being reduced to approximately 85% of the total yield in the control (no-shading) (RDA, 2017). Smith et al. (1984) also confirmed the negative effect of shading on cucumber yield, however, there were reports to the contrary (Naraghi and Lotfi, 2010; Kitta et al., 2012).
In our study, the light transmittance of cover materials by PM during the spring season did not affect significantly the vegetative growth of cucumber plants, however, reduced the total yield of cucumber. After 42 DAT, the shoot fresh weight of cucumber plants was promoted by increasing the reduced light transmittance and the cumulative yield of cucumber in the control was much higher than those in the reduced light transmittance treatments. Our experiment was conducted during the spring season with the high occurrence of PM, however, the air temperature inside the greenhouse frequently exceeded 30℃ during the day from March 21. The average daily maximum temperatures from March 21 to April 17 were 34.7, 34.8, 33.9, and 33.3°C for the control, 10, 20, and 30% reduced light transmittance treatments, respectively (Fig. 6). All of the treatments except the 30% reduced light transmittance had days with maximum air temperatures in excess of 40oC. The average times exposed to high temperatures above 30oC were 3.35, 2.90, 2.72, and 2.27 hours/day in the control, 10, 20, and 30 reduced light transmittance treatments, respectively.
As cucumber is a low-temperature crop (Woo et al., 2014; Balal et al., 2015), the cucumber plants grown under the high solar irradiance conditions (no or low decrease in light transmittance by PM) showed a delay in growth at the end of the experimental period due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures. Although the vegetative growth of cucumber plants was reduced by the high air temperatures under the high solar irradiance conditions, the total yield of cucumbers was highest in the control. During the cultivation period, the reduction in light transmittance of the cover materials by PM resulted in the decreased light intensity inside the PE tunnel. We adjusted the light transmittance of the PE tunnel by measuring the light intensity before and after dust was applied to the cover material, therefore, the cucumber plants in the 10, 20, and 30% reduced light transmittance treatments received the light at an intensity of 10, 20, and 30% lower than that of the control. Marcelis (1993) reported that the prolonged low irradiance condition resulted in a lower proportion of biomass allocated to fruit and a decrease in the growth rate of individual fruits and the number of fruits growing simultaneously on one plant. And, in the cucumber at the ripening stage, photosynthetic and antioxidant enzymes decreased under low light intensity condition (Yang et al., 2015).
Conclusion
In this study, we confirmed that the light transmittance of cover material for a greenhouse could be reduced by the frequent occurrence of PM, and the reduction in the light transmittance of PO film by PM was lower than that of PE film. For the cucumber cultivation during the spring season, the reduction in light transmittance of cover material by PM could reduce the delay in vegetative growth by high temperature stress inside the greenhouse from late March, however, affected negatively the total yield of cucumbers due to the reduced photosynthesis under the low light intensity conditions. Our results showed that under the conditions where PM frequently occurs, the crop grown in greenhouses could indirectly receive the negative impact on yield due to the reduction in light transmittance of cover materials by PM.